In the long run, it will also help you in your daily work with your website. To help you choose the right system, we have already written the blog post "The right choice: Which is the best CMS?" Today, we take a look at two of the most popular systems and compare them. Who is ahead - WordPress or Typo3?
When it comes to market share, there is a clear winner: WordPress is in first place with a clear gap to the following ranks. There are big differences in the distribution of Typo3 depending on the country, the program is particularly popular in German-speaking countries.
In the following two sections, we will take a closer look at the WordPress and Typo3 systems and provide information on their origins and technology. We will also take a look at the main features of the programs - initially without dividing them into advantages and disadvantages. What is useful for one project may not be necessary for another.
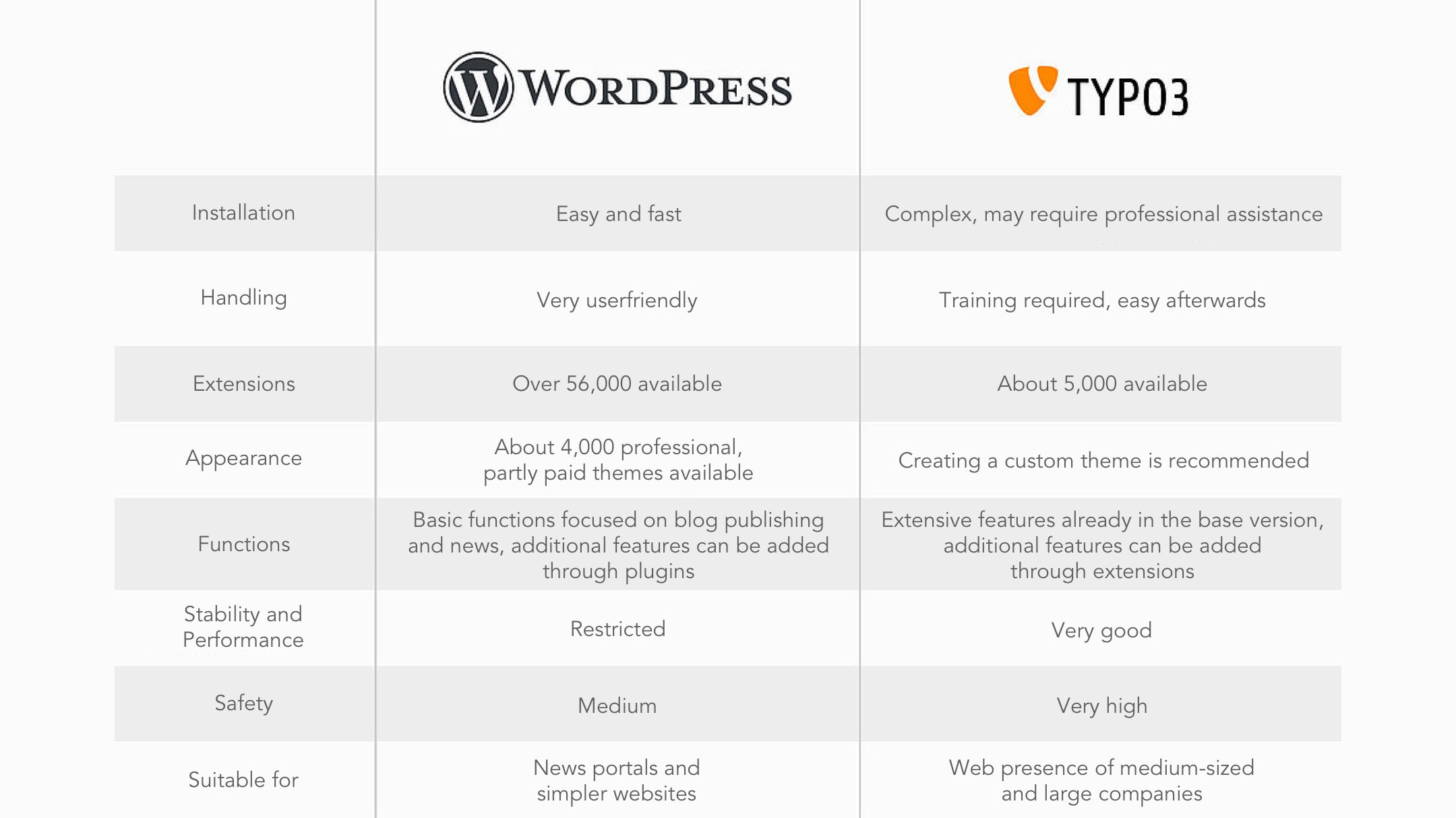
For a quick overview of the main features of WordPress and Typo3, here is our comparison table.
Based on the open source program b2/cafelog, originally written by Michel Valdrighi, Matthew Mullenweg and Mike Little developed WordPress in 2003. The goal: a weblog software that would be easy to use, flexible and easily customizable. The first stable version was released under the GNU General Public License on January 3, 2004.
Over the years, the functionality of WordPress has been expanded and the system has evolved from a simple blog software to the most popular content management system. Its success is largely due to the large community that has been programming extensions and improvements to WordPress almost non-stop. It would have taken one person nearly 400 years to develop the current version and the available plugins. (As of May 2020)
Here is a look at the most important features:
WordPress is based on the PHP scripting language and requires a MySQL or MariaDB database, which should be installed on the host of your choice. If these requirements are met, installation is very simple: According to the developers, it takes less than five minutes from downloading the source code package to creating the site.
The intuitive use of WordPress is what makes the CMS so popular. Installation and operation are simple and can be done by a layman. If you have any questions, the community can help you in various question forums. For use on the go, there are special apps that allow access via smartphone.
With over 56,000 plugins available in the official WordPress directory, there is something for everyone. You should always make sure that your tools are up to date: outdated plugins are often vulnerable to hackers.
The archive of design templates for WordPress is unique: There are now around 4,000 professional themes. In addition to the pre-installed templates, there are many different variations for every taste on the developers' websites and via the built-in theme browser - both free and paid.
The basic version of WordPress has only a few basic functions: In addition to the easy creation and editing of blog posts and static pages, it offers the ability to add comments and manage links. There is also a simple content management system with five user roles and a multi-site function. The creation of multilingual pages is not supported. However, you can customize the system to your individual needs using the numerous plugins available. There are areas that you should definitely expand, such as loading time, SEO, backups, privacy and security. Other features are very specific, such as e-commerce, membership, and social media.
Because WordPress was designed as a dynamic blogging system, the basic version does not include caching and will quickly reach its limits with high traffic. A plugin can help and speed up loading times. At the same time, you should be careful with the number of plugins you install, as too many will slow down your site. For good performance, the rule is: as few as possible, as many as necessary.
Due to its widespread use, WordPress is particularly popular with hackers and their number one target. To keep your site as secure as possible, you need to keep it updated and avoid too many plugins from different sources. These are the most common security holes - either because of vulnerable code or missing updates.
In 1997, Dane Kasper Skårhøj began developing software that would allow customers to create and maintain websites without any knowledge of HTML. After a brief use as a commercial system for an advertising agency, the first official version of Typo3 was released in 2001 as an open source project under the GNU General Public License. Three years later, the Typo3 Association was founded: This non-profit association based in Switzerland coordinates the ongoing development of the CMS.
Typo3 is regarded as an Enterprise Content Management System that is often used - especially in Europe - to create and manage complex Internet projects. But why?
The core of TYPO3 is written in the scripting language PHP, and the system specific configuration language TypoScript is also used. The database can be MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL or Oracle. Since the initial setup requires specialized knowledge, you should contact a digital agency.
You will need a specialist - internal or external - to install and maintain a Typo3 website, but not for editorial maintenance. Allow some time for training, after which you will be able to use the full functionality of the CMS.
There are currently about 5,500 extensions in TER alone, the public extension repository, written by an estimated 2,000 programmers.
There are only a few design templates for Typo3, most companies have developed their own theme.
Typo3 impresses with its wide range of functions: Even the basic version includes numerous options such as multilingualism, multi-site and multi-domain capability as well as complex rights management. A workflow management function simplifies the approval process, and open interfaces allow easy integration with classic business applications such as CRM and ERP systems.
Typo3 impresses with its clean code base, which meets even the most demanding requirements and ensures flawless, stable performance. The caching function, which comes standard, also has a positive effect on page loading times.
The Typo3 Association is responsible for the security of the system. Their security team monitors further development and responds promptly with security updates when problems arise. There is also a regular Long Term Support (LTS) version, which is provided with security and maintenance updates free of charge for 3 years. After that, it is possible to use the version for another 3 years as part of a paid Extended Long Term Support (ELTS) version. As long as you use one of these supported versions, the risk of successful attacks on your website is low.
Both content management systems have their pros and cons: WordPress is now much more than a simple blog system and has expanded its capabilities greatly in recent years. The system can do a lot, but not everything - its shortcomings are especially painful for complex corporate websites, while its advantages are mainly convincing for news portals and smaller projects. With Typo3, the situation is exactly the opposite: The CMS is far too powerful and complex for simple websites, but scores with medium and large companies in the areas of functionality, security and stability.
If you want to read more about CMS, we recommend our article for next week "CMS Comparison Part 2: Typo3 vs. Drupal". In principle, it is advisable to decide on a case-by-case basis which system best meets your needs. Perhaps your needs are more complex: a corporate website with an attached blog, a community portal with user-generated content, an online shop with content-based advice... Ask us for a custom solution, we'll be happy to help. You can reach us by phone at +49 711 184 206-0 or by email at hello@wus.de.